Table of Contents
Introduction
Picture your website as a map, and Googlebot as an explorer trying to navigate it. Crawl errors are like blocked paths or dead ends that hinder the explorer. These errors affect your site’s performance and ranking in search engines. Fixing Crawl Errors in GSC is essential for maintaining a smooth user experience and optimizing your site’s visibility. Using Google Search Console (GSC), you can efficiently diagnose and fix these issues. Let’s dive into practical solutions, with examples.
What Are Crawl Errors?
Crawl errors occur when Googlebot or other search engine crawlers encounter problems while accessing your website. This leads to incomplete indexing, lower rankings, and poor user experience.
Example:
A user tries to access https://yourwebsite.com/about-us but encounters a 404 error because the page doesn’t exist or the URL is misspelled.
Types of Crawl Errors in GSC with Examples and Solutions
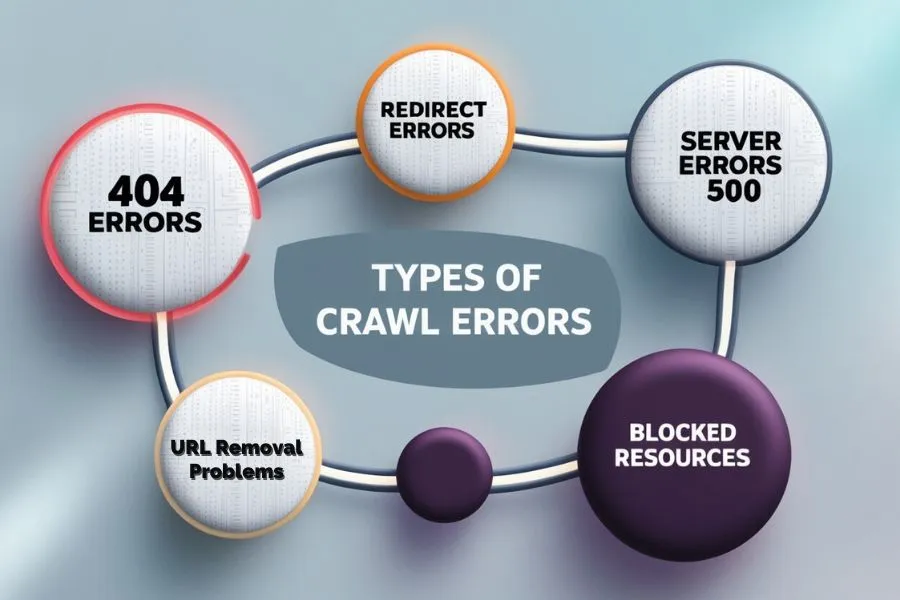
1. 404 Errors (Not Found)
What Happens:
When a page is missing or deleted, users and bots land on a “Page Not Found” error.
Example:
https://yourwebsite.com/contact-us was deleted without a redirect.
Solution Process:
- Redirect: Implement a 301 redirect to a relevant page, like https://yourwebsite.com/contact.
- Use tools like Yoast SEO (for WordPress) or .htaccess for manual redirects.
- Fix Internal Links: Update any links pointing to the deleted page to avoid repeated errors.
- Custom 404 Page: Create a helpful 404 page with links to popular or relevant sections.
2. Redirect Errors
What Happens:
Redirect loops or chains confuse users and bots, causing abandonment and crawl budget wastage.
Example:
Page A → Page B → Page C → Page A (redirect loop).
Solution Process:
- Check Redirects: Use tool like Screaming Frog to identify.
- Simplify Paths: Redirect Page A directly to the final destination (e.g., Page C).
- Test Redirects: Verify fixes using GSC’s URL Inspection Tool or HTTP Status Checker.
3. Server Errors (5xx)
What Happens:
Server issues, like downtime or overload, prevent crawlers from accessing your website.
Example:
Googlebot tries to load https://yourwebsite.com/shop but encounters a 503 error due to server overload.
Solution Process:
- Check Server Logs: Use hosting control panels or analytics tools to find the cause.
- Upgrade Hosting: Opt for higher-tier hosting plans if your traffic exceeds the server capacity.
- Optimize Website: Compress large images using tools like TinyPNG and leverage caching plugins (e.g., WP Rocket).
4. URL Removal-Related Problems
What Happens:
Improper use of the URL removal tool in GSC can block essential pages from search results.
Example:
Accidentally blocking https://yourwebsite.com/blog via the URL removal tool.
Solution Process:
- Check URL Status: In GSC, go to Removals and inspect the blocked URLs.
- Cancel Unnecessary Requests: If critical URLs are removed, revoke the request.
- Submit Pages for Reindexing: Use GSC’s URL Inspection Tool to request indexing.
5. Blocked Resources
What Happens:
CSS, JavaScript, or media files are blocked by robots.txt or other settings, impacting page rendering.
Example:
robots.txt contains:
javascript
Copy code
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-content/
This blocks essential files like theme CSS or JavaScript.
Solution Process:
- Edit Robots.txt: Update the file to allow access to critical resources:
javascript
Copy code
User-agent: *
Allow: /wp-content/themes/
- Test Changes: Use GSC’s Robots Testing Tool to verify.
- Validate Rendering: In GSC, check how Google sees your page under URL Inspection > View Crawled Page.
Diagnosing Crawl Errors in GSC
Step-by-Step Example:
1. Open the Coverage Report:
- Go to GSC → Coverage → Identify “Error” and “Excluded” tabs.
2. Review Error Types:
- Check the description, such as “Submitted URL not found (404)” or “Blocked by robots.txt.”
3. Inspect URLs:
- Use URL Inspection Tool to analyze specific issues.
- Example: A page showing “Crawl Anomaly” might have intermittent server issues.
Fixing Crawl Errors in GSC with Real Examples
Fixing 404 Errors
Example:
https://yourwebsite.com/services/web-design returns 404 after redesign.
Steps:
- Redirect to https://yourwebsite.com/services.
- Update all backlinks pointing to the old URL.
Resolving Redirect Errors
Example:
https://yourwebsite.com/product redirects to https://yourwebsite.com/item which redirects to https://yourwebsite.com/shop.
Steps:
- Combine into a single redirect:
https://yourwebsite.com/product → https://yourwebsite.com/shop.
Handling Server Errors
Example:
500 Internal Server Error occurs during high-traffic hours.
Steps:
- Upgrade hosting to a scalable VPS or cloud hosting like AWS.
- Use CDNs (e.g., Cloudflare) for better load management.
Monitoring and Maintaining Crawl Health
- Set Alerts: Enable email notifications in GSC for new crawl issues.
- Use SEO Tools: Regularly audit your site with Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Screaming Frog.
- Review Robots.txt: Ensure it’s updated with no unnecessary disallow rules.
How Google Search Console Features Help SEO
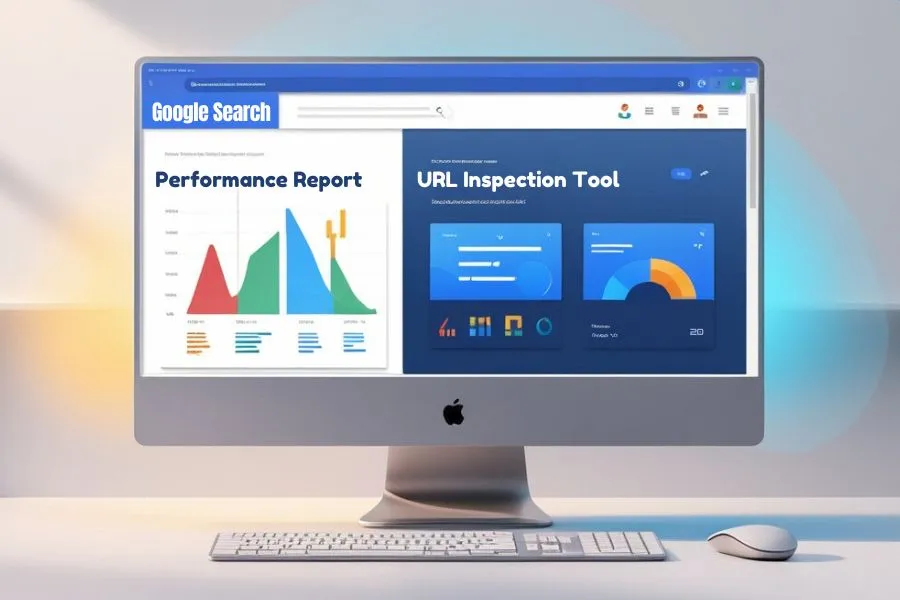
Example 1: Performance Report
Track how crawl error fixes improve clicks, impressions, and rankings.
Example 2: URL Inspection Tool
Confirm fixes are effective by submitting corrected URLs for validation.
Conclusion
Fixing crawl errors not only improves SEO but also ensures a seamless experience for users and bots. By actively monitoring and resolving issues, you can maintain a robust and error-free website.
FAQs
1. What are crawl issues in GSC?
Crawl issues are obstacles preventing Googlebot from properly accessing or indexing your site.
2. How do I fix 404 errors?
Redirect broken URLs to relevant pages, update internal links, and create a custom 404 page.
3. What does the URL removal tool do?
It temporarily hides pages from search results but doesn’t delete them permanently.
4. Why are server errors bad for SEO?
They waste crawl budget and can signal to Google that your site is unreliable.
5. Can redirect errors hurt rankings?
Yes, redirect chains or loops confuse bots and users, reducing crawl efficiency and user satisfaction.

